A novel solution to tackle deoxynivalenol in feed

β-glucans have a variety of biological functions, including improving the intestinal environment, modulating immunity and enhancing antioxidant capacity. The protective effect against deoxynivalenol (DON) (an immuno-toxic mycotoxin) of a purified yeast fraction enriched with β-glucans was further tested in porcine in vitro and ex
vivo models.
MYCOTOXIN SPECIAL 2023 – read all articles
Among mycotoxins, DON, is one of the most prevalent and occurs worldwide in feed. DON-contaminated feed may be responsible for several adverse effects with a major impact on animal health and production. Once ingested by animals, DON initially interacts with the intestinal epithelium, leading to intestinal damage and impaired immune function. Pigs are the most sensitive animals to DON. The use of mycotoxin detoxifying agents as feed additives is advantageous in reducing the toxic effects of mycotoxins in pigs and, at the same time, can reduce crop wastage and enable more sustainable use of animal feed. There are many mechanisms by which mycotoxin detoxifying agents attenuate the toxic effects of mycotoxins in animals. One of those mechanisms is adsorption, where the mycotoxin interacts with another molecule (adsorbent) becoming non-absorbable by the animal’s body. Another mechanism is to use these agents to boost immune function and gut health, making the animal less susceptible to the toxic effects of mycotoxins. Therefore, we focus on the use of Safglucan, a patented yeast fraction enriched with β-glucans, to reduce DON-induced inflammation, and improve intestinal integrity and ultimately improve animal health. Considering that DON, once ingested by the animal, initially interacts with the intestinal epithelium leading to intestinal damage, models focusing on the integrity of this epithelium and immune function have been used. The study was conducted in vitro on IPEC-J2 porcine intestinal cells and ex vivo on porcine jejunum explants.
Effect of DON on IPEC-J2 cells
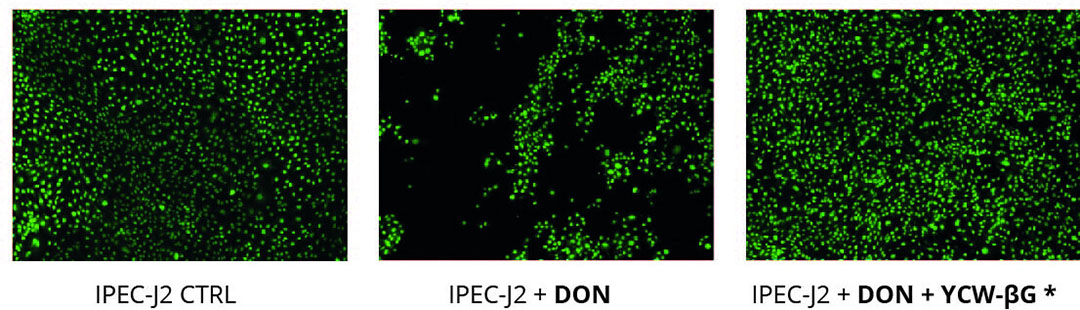
The intestinal barrier function is maintained by intercellular structures such as tight junctions. The trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) is considered as an indicator of the epithelial integrity and thus of the organisation of tight junctions. We demonstrated a reduction of the TEER of the IPEC-J2 cell line after DON exposure with 50% decrease in DON treated cells compared with control cells. Addition of Safglucan, limits the decrease of the TEER in presence of DON with only 25% decrease compared with control cells after 8 hours of exposure. Illustration in electronic microscopy of impact of DON on epithelial integrity of IPEC-J2 cells is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 – Effect of DON and yeast fractions on gut barrier integrity captured under fluorescence microscopy. The images were taken after 24h of exposure to 10µM DON.
Cytokines play a major role in the immune and inflammatory response following exposure to DON. Thus, their balance is important for protection against DON. In order to assess the pro-inflammatory activity exerted by DON on intestinal cells, the expression levels of IL-8 mRNAs were measured. After 24 h of exposure to DON, a significant increase in the expression of IL-8 was observed (fold increase x8.2). In the presence of the yeast fraction, the increase in the expression of IL8 was significantly less marked (fold increase x4.2).
These effects were observed following exposure to DON and were expected and consistent with previous IPEC-J2 studies as well as necrotic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract reported in chronic or acute toxicity studies.
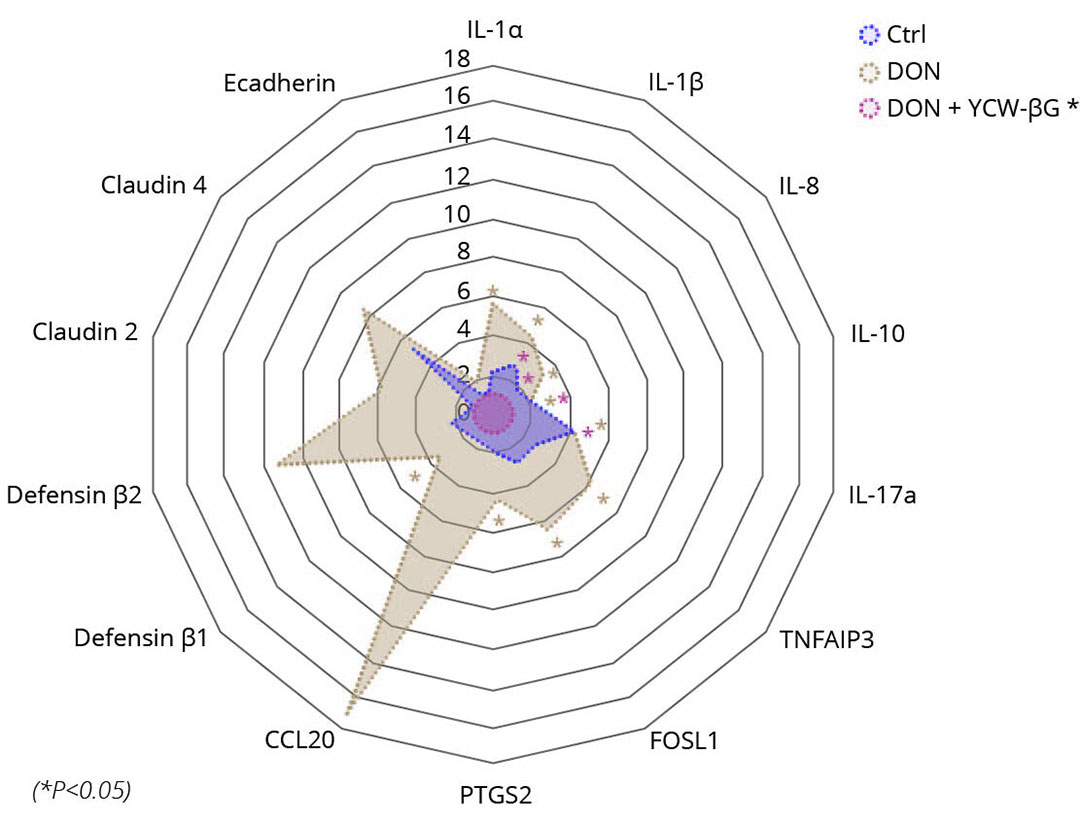
Figure 2 – Effect of DON and yeast fractions on the expression of different genes in pig explants.
Effect of DON on porcine jejunal explant
The effect of DON on the development of inflammation was investigated by measuring the mRNA expression levels of inflammatory genes such as interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-8 (IL-8), IL-10, IL-17a, IL-1α, CCL20, PTGS2, TNFAIP3, FOSL1, and also tight junction protein genes like claudin 2, claudin 4 and E-Cadherin as well as defensin genes (DEF β1, DEF β2 and DEF β3). The results are shown in Figure 2. As expected, exposure of explants with 10 μM DON for 4h leads to an increase in the production of transcripts of inflammatory-related genes. Thus, we observed a significant increase in the production of transcripts for the following genes: IL-1β, IL-8, IL-17a, IL-1α, FOSL1, TNFAIP3, PTGS2 and IL-10. There has been a trend towards an increase in the production of transcripts for the CCL20 and IL-22 genes in response to exposure of explants with 10 μM DON. The use of the yeast fraction-based solution alone did not modify gene expression at any dose used. It was noted that the solution based on yeast fractions has significantly down modulated the expression of transcripts for the IL-1β and IL-8. A downward trend was also observed for IL-1α, PTGS2, CCL20 and FOSL1. No effect of the yeast solution was observed on expression of the IL-10, IL-17, TNFAIP3 and IL-22 genes when the explants were co-exposed with 10μM DON.
Benefits of using yeast enriched with β-glucans
This study aimed to evaluate the toxic effects of DON on the intestine of pigs and the potential benefits of a yeast fraction enriched in β-glucans in the protection against these deleterious effects, using in vitro and ex vivo approaches. DON impairs the epithelial integrity as observed in the IPEC-J2 cells, and this negative impact was counteracted in presence of a yeast β-glucan. The solution based on yeast fractions tested under these experimental conditions also modulated the expression of genes associated with inflammatory responses by decreasing their expression compared to explants and cells only exposed to DON. Overall, the results showed that Safglucan, the β-glucan enriched yeast fractions, reduced DON-induced inflammation and reinforce intestinal epithelial integrity.
References available upon request.






