4 steps for an optimal phytogenic gut health solution

Phytomolecules with digestive, antimicrobial, and gut health-promoting characteristics are an ideal solution to compensate for reduced antibiotic use in critical periods. However, not all phytogenic products are equally able to provide such benefits.
Part of the Gut Health 2022 Special
For an optimal phytogenic gut health solution, it is crucial that:
phytomolecule levels are standardised for consistent results
they show the highest stability during stringent feed processing (high temperatures and pressure), despite often being highly volatile
the phytomolecules are preferably completely released and available in the animal for best effectiveness.
 Standardised phytomolecules
Standardised phytomolecules
When phytomolecules are extracted from plants, results vary depending on genetic variation in the plants, weather, soil, and harvest time, but also drying, storage, and extraction methods. For example, thyme oil can contain between 22 and 71% of the relevant phenol thymol.
Modern technology produces standardised phytomolecules with the highest degree of purity and lowest possible batch-to-batch variation. Environmental and economic sustainability also benefit from this reliable and cost-effective sourcing technology.
Using such highly standardised phytomolecules enables the production of phytogenic-based feed supplements of consistently high quality.
 Selecting suitable phytomolecules
Selecting suitable phytomolecules
Some phytomolecules support digestion, while others act against pathogens or are antioxidants. For optimal gut health in animal production, it is essential to reduce pathogens while promoting beneficial microbes. The decrease of pathogens in the gut not only decreases the risk of enteritis but also eliminates inconvenient competitors for feed.
To find the best combination of phytomolecules for achieving this effect, one must evaluate many different ones concerning their structure, chemical properties, and biological activities. Availability and procurement costs are further factors to consider. Then, one tests various mixtures of the most suitable phytomolecules for their effectiveness. Identifying synergistic or antagonistic effects is essential to decide on the best-performing blend.
 Protecting the ingredients
Protecting the ingredients
Many phytomolecules are inherently highly volatile and need protection from the stringent feed hygienisation process in the feed mill. For intestinal release, a carrier with capillary binding together with a protective coating offers an effective solution. It protects the ingredients during feed processing, but the digestive tract’s pH and enzymes open the coating, and the phytomolecules can act at the right site.
Ventar D is a next-generation solution for gut health optimisation. A scientific study assessed its stability in the pelleting process, compared to 2 other leading phytogenic feed supplements.
All phytogenic feed supplements were added to standard broiler feed at the producer’s recommended inclusion rate. The tests took place under conditioning times of 45, 90, and 180 seconds and pelleting temperatures of 70, 80, and 90°C (158, 176, and 194°F). After cooling, triplicate samples were collected and analysed. The respective marker substance was analysed through GC/MS to measure the recovery rate in the finished feed. The phytomolecule content of the mash feed (before pelletisation) was used as a baseline and set to 100% recovery. The recovery rates of the pelleted feed were evaluated relative to this baseline.
Ventar D showed the highest stability of active ingredients, with recovery rates of 90% at 70°C/45 sec. or 80°C/90 sec and 84% at 90°C/180 sec. The production technology ensures that the active ingredients are protected well throughout pelletisation.
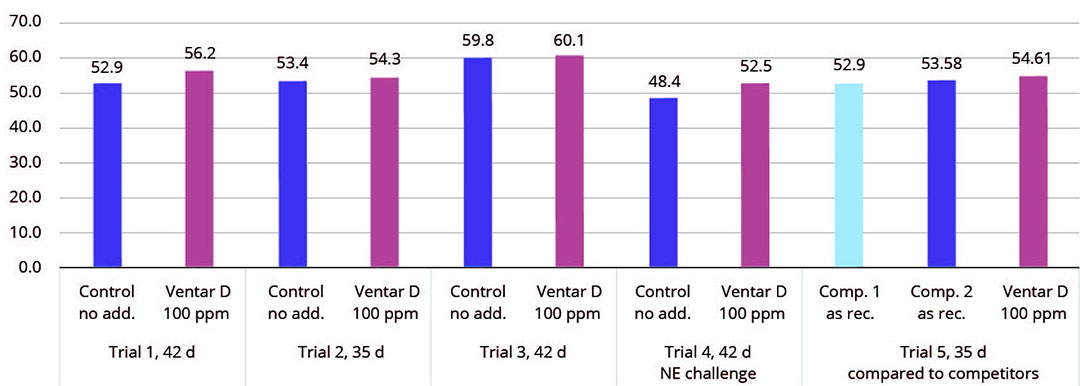
Figure 1 – Average daily gain (g) – results of several trials conducted with broilers.
 Delivering benefits
Delivering benefits
In vitro studies proved the targeted antimicrobial activity of Ventar D, showing stronger activity against common enteropathogenic bacteria while sparing the beneficial ones. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity supports better gut barrier functioning. Better gut health leads to higher growth performance and improved feed conversion, which was demonstrated in several broiler trials (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 2 – FCR results of several trials conducted with broilers.
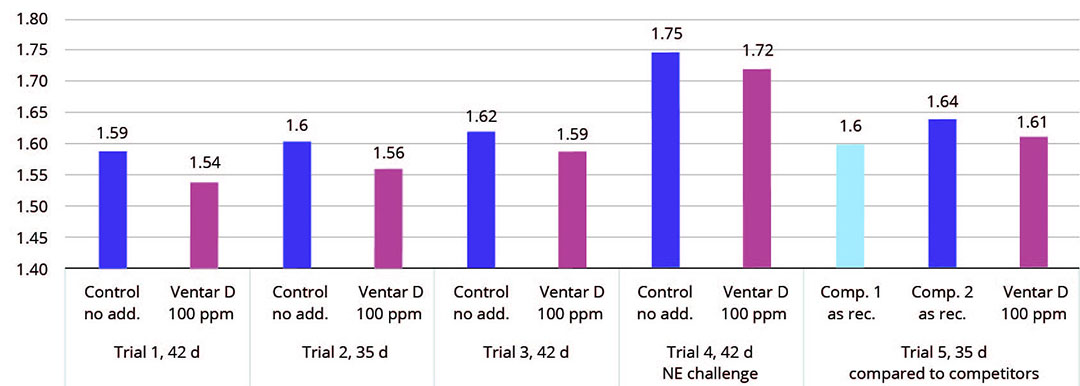
In the tests, a group supplemented with the product at 100 g/t of feed was compared to either a control group with no feed supplement or groups supplied with competitor products at the recommended inclusion rates.
Compared to negative control groups, the Ventar D group consistently showed a higher average daily gain of 0.3-4.1 g (0.5-8.5 and a 3-4 points better feed conversion. Compared to competitor products, the product generated 1-1.7 g (2-3%) higher average daily gain and a 1 to 3 points better FCR.
Standardisation and new technologies
Combining standardised phytomolecules and optimal active ingredient protection leads to superior product stability during feed processing. The higher amount of active ingredients arriving in the gut improves gut health and increases the production performance of the animals. The 4 steps for an optimal phytogenic gut health solution show how we can harness the power of phytomolecules to achieve higher farm profitability.
References are available on request.